This is one of the common interview questions whether you have a beginner or a more experienced person. The below example has duplicate values in the name column and we need to remove the duplicate value based on business requirements.
We have many ways to remove the duplicate values from the value, we will look at all methods one by one.
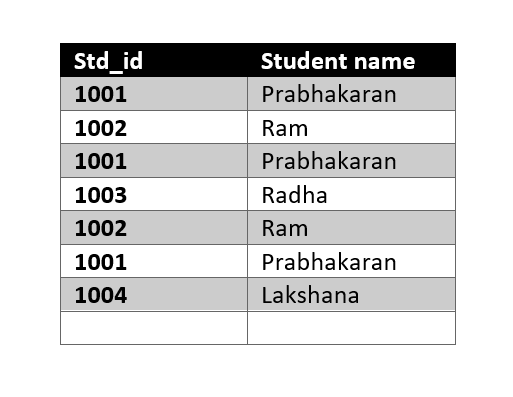
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[studentDetails]( [Std_id] [int] NOT NULL, [Std_Name] [varchar](50) NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GO INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1001, N'Prabhakaran') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1002, N'Ram') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1001, N'Prabhakaran') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1003, N'Radha') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1002, N'Ram') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1001, N'Prabhakaran') INSERT [dbo].[studentDetails] ([Std_id], [Std_Name]) VALUES (1004, N'Lakshana')
Method 1: Using CTE
What is CTE?
What is Rank Function?
-- BEFORE Removing Dupliate SELECT * FROM [studentDetails] ------------------------------------------------------- ;WITH StudentCTE AS ( SELECT Row_NUMBer() OVER(PARTITION BY Std_id ORDER BY Std_id ) AS [RNumber], * FROM [studentDetails] ) DELETE FROM StudentCTE Where [RNumber] > 1 ------------------------------------------------------- -- AFTER Removing Dupliate SELECT * FROM [studentDetails]
OutPut
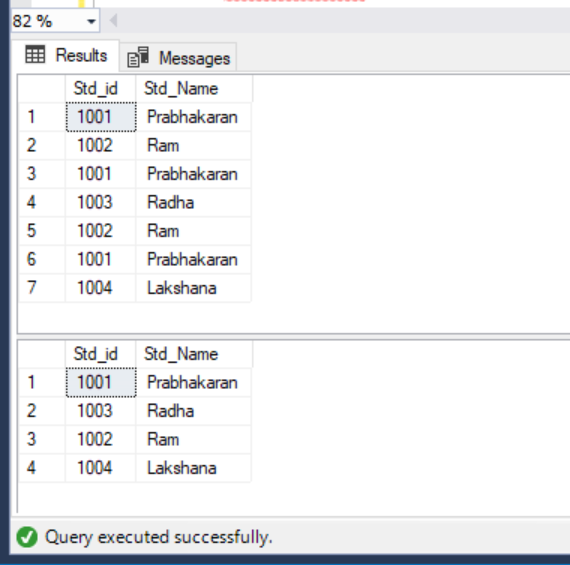
The above result you will get after removed the duplicates
Method 1: Using TOP Keyword
if you want to delete one duplicate record from the table, we can directly use the TOP keyword to delete the records.
DECLARE @Name Varchar(100) = 'Ram' DELETE FROM studentDetails Where Std_Name = @Name
if you want to delete all duplicate records from the table. we can go with each row-wise to process to delete the record.
DECLARE @Std_Name VarChar(1000)
DECLARE db_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT DISTINCT Std_Name FROM studentDetails
OPEN db_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @Std_Name
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
IF EXISTS ( SELECT Count() FROM studentDetails Where Std_Name = @Std_Name HAVING Count() >1 )
BEGIN
DELETE TOP(1) FROM studentDetails Where Std_Name = @Std_Name
PRINT @Std_Name
END
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @Std_Name
END
CLOSE db_cursor
DEALLOCATE db_cursor
NOTE: As per my suggestion we can use CTE to delete the duplicate records.
Method 3: Using ROWSET Keyword
What is ROWSET?
Basically, by using the ROWCount Set function we can restrict the specified numbers of returns. and also need to off once the Rowcount is used.
You can see the below result, by using ROWCOUNT we are restricted to process only one record in this transaction to delete the record.
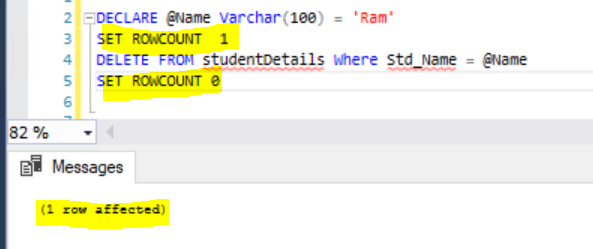
Query
DECLARE @Name Varchar(100) = 'Ram' SET ROWCOUNT 1 DELETE FROM studentDetails Where Std_Name = @Name SET ROWCOUNT 0
Thank You.!!







Leave a Reply